|
» Bearing Stress
BEARING STRESS is the stress caused by one part acting directly on another. Bearing stress, as the name implies, is a compressive stress and is equal to the Bearing Force divided by the Bearing Area.
In typical Bolted or Riveted Connections we are mainly interested in the AVERAGE BEARING STRESS, sB, which is the Bearing Force divided by the Projected Area of the Fasteners:
| sB = |
Bearing Force

Projected Area
|
|
|
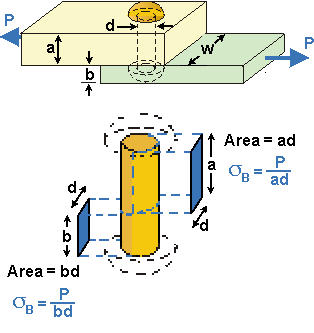
Projected Areas of Rivet.
|










